How the S&P 500 became the gold standard for long-term investing
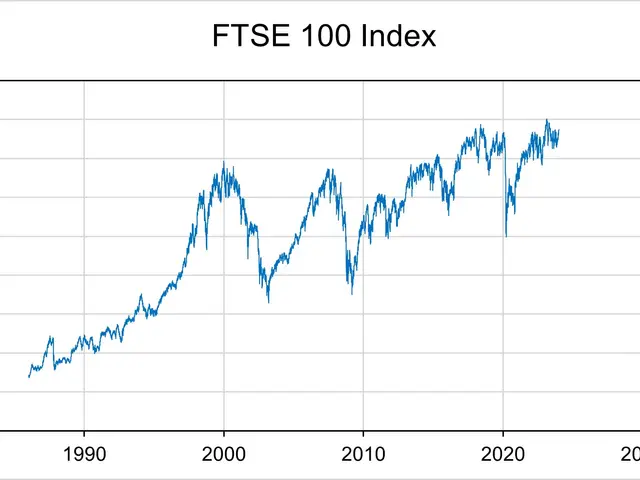
The S&P 500 remains one of the most reliable ways to invest in the stock market. Launched on 4 March 1957, it tracks 500 of the largest US companies, chosen for their size and liquidity. While not every firm in the index performs perfectly, its long-term returns have made it a favourite among investors.
The index was not built with fixed founding members like a company. Instead, Standard & Poor's selected its initial 500 constituents based on market value and trading activity. No official list of the original companies exists, as the lineup has always evolved over time.
Today, the S&P 500 includes some of the world's biggest names. Tech giants like Microsoft, Apple, and Amazon dominate the top spots. Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway also ranks among the leading stocks. In healthcare, UnitedHealth Group and Johnson & Johnson stand out as key players. Investors can easily track the index through low-cost ETFs. These funds replicate the S&P 500's performance without the need to buy each stock individually. Over decades, the index has delivered an average annual return of around 10%. Sustaining such growth over time can turn modest savings into substantial wealth.
The S&P 500 offers a straightforward way to invest in a broad range of high-quality companies. Its consistent long-term performance has helped many build wealth through steady growth. For those seeking a balanced and low-maintenance approach, the index remains a popular choice.